Back
GEO vs SEO in 2026: A Practical Task Comparison
A Task-by-Task Breakdown of What Works in Search Rankings vs AI Citations
22 Ara 2025
The way people search for information online is changing fast. While Google and traditional search engines still dominate, AI-powered tools like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google's AI Overviews are reshaping how users find answers. This shift means content creators need to understand both SEO (Search Engine Optimization) and GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) to stay visible.
SEO has been the backbone of digital marketing for decades, focusing on ranking high in search results through keywords, backlinks, and technical optimization. GEO is about getting your content selected and cited by AI systems that generate direct answers instead of just listing links.
If you're still relying only on traditional SEO tactics, you're missing a huge opportunity. AI engines don't just rank pages; they extract, synthesize, and present information in entirely new ways. Understanding how these two approaches differ, and where they overlap, is essential for anyone serious about online visibility in 2026 and beyond.
What Is SEO and GEO? What Are the Main Differences?
SEO is the practice of optimizing your website and content to rank higher in traditional search engine results pages (SERPs). When someone types a query into Google, Bing, or another search engine, SEO determines which pages appear at the top. The goal is simple: drive organic traffic by making your content discoverable, relevant, and authoritative.
The core elements include targeting the right keywords, building quality backlinks, optimizing meta tags, ensuring fast page speed, and creating content that matches user intent. Success gets measured by rankings, click-through rates, and the amount of traffic your site receives.
GEO, or Generative Engine Optimization, is designed for AI-driven search platforms. Instead of displaying a list of links, generative engines like ChatGPT, Google's AI Overviews, and Perplexity provide synthesized answers by pulling information from multiple sources. GEO focuses on making your content the source that AI engines cite, reference, or include in their responses.
Aspect | SEO | GEO |
Primary Goal | Rank higher in search results to drive website traffic | Get cited and referenced in AI-generated answers |
How It Works | Algorithms crawl, index, and rank pages based on keywords and backlinks | AI extracts and synthesizes information from multiple sources to answer queries |
Success Metric | Rankings, organic traffic, click-through rate | Citations, brand mentions in AI responses, AI visibility |
Content Format | Keyword-optimized articles with hierarchical structure (H1, H2, H3) | Answer-focused chunks, Q&A format, self-contained sections |
User Behavior | Users click through to websites and browse content | Users receive direct answers without visiting websites |
The main difference comes down to how users interact with results. In traditional search, users click through to websites. With generative AI, users often get their answer directly without ever visiting a site. SEO is about competing for position on a results page, while GEO is about being selected as a trusted source within an AI-generated answer.
How Do Traditional Search Engines Rank Content?
Traditional search engines like Google use complex algorithms to determine which pages deserve to rank at the top. While the exact formulas are proprietary and constantly evolving, the core principles have remained fairly consistent.
Relevance matters most. Google crawls billions of web pages and indexes them based on keywords, topics, and semantic relationships. When you search for something, the algorithm matches your query to pages that contain relevant terms and related concepts. Using your target keyword in the title, headings, and body text signals to Google that your page is about that topic.
Authority plays a huge role too. Google evaluates authority primarily through backlinks, which are links from other websites pointing to yours. The more high-quality sites that link to your content, the more Google trusts it. A link from a major news outlet or a .edu domain carries far more weight than a link from a random blog.
User experience signals tell Google whether users found what they were looking for. Metrics like bounce rate, time on page, and click-through rate all factor in. Technical elements like page speed, mobile-friendliness, and secure HTTPS connections also matter. Google favors comprehensive, well-researched content that fully answers a query while penalizing thin or outdated material.
How Do Generative AI Engines Select and Cite Content?
Generative AI engines work differently from traditional search. Instead of ranking pages and letting users choose, they synthesize information from multiple sources and present a direct answer. Tools like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google's AI Overviews, and Gemini pull data from the web, process it, and generate responses that aim to fully satisfy the user's query.
The selection process starts with understanding intent. AI models are trained to interpret natural language, which means they don't just match keywords but grasp the meaning and context behind a question. If someone asks "How do I improve my Google Ads performance?", the AI understands they're looking for actionable tips, not just a definition.
Once the AI understands the query, it searches through indexed content to find relevant sources. But instead of ranking them in a list, it evaluates which sources provide the clearest, most authoritative, and most up-to-date information. Content that directly answers the question, uses clear language, and includes supporting data is more likely to be selected.
Citation and attribution are key in GEO. When a generative engine includes information from your site, it may reference you by name, link to your page, or attribute the insight to your brand. This matters for AI visibility, as getting cited by AI means your brand gets exposure even if users never click through to your website.
AI engines favor structured, chunk-based content. Each section of your article should function as a self-contained answer. If you have a heading like "What is a good CTR for Google Ads?", the paragraph beneath it should immediately provide a clear answer, followed by context or examples. AI can extract that chunk and present it without needing the entire article.
Recency and trust signals matter too. Generative engines prioritize content that cites recent data, references authoritative sources, and demonstrates expertise. Including statistics from 2024 or 2025, linking to trusted publications, and showcasing real-world examples all improve your chances of being selected.
Keyword Optimization in SEO vs Intent Mapping in GEO
In traditional SEO, keyword optimization drives everything. You research high-volume keywords, analyze competition, and strategically place them throughout your content. The primary keyword goes in the H1, meta title, and introduction. Secondary keywords and long-tail variations appear in subheadings and body paragraphs.
Tools like Google Keyword Planner help identify which terms have search volume and how difficult they are to rank for. You look for opportunities where demand is high but competition is manageable. Once you've selected your keywords, you optimize on-page elements, build backlinks with keyword rich anchor text, and track your rankings over time.
Aspect | SEO Keyword Strategy | GEO Intent Strategy |
Focus | Exact keyword matching and search volume | User intent and related question clusters |
Placement | H1, meta title, introduction, H2s, conclusion | Natural language throughout, Q&A sections, FAQ |
Variations | Long-tail keywords and synonyms | Conversational phrases and follow-up questions |
Success Indicator | Keyword rankings and organic traffic | AI citations, brand mentions in AI responses |
GEO takes a different approach. Instead of focusing solely on keywords, you map user intent and anticipate the fan of related queries that stem from a single search. For example, if someone searches for "Google Ads optimization," they might also want to know "What is a good optimization score?", "How to improve CTR?", or "What are the best bidding strategies?" These questions don't all share the exact keyword, but they're part of the same intent cluster.
Tools like AlsoAsked.com and AnswerThePublic become essential for GEO. They visualize how one query branches into dozens of related questions. Your content should address not just the main keyword, but the surrounding context and follow-up questions that a user might have. Learn more about writing for AI engines to master this approach.
In SEO, you might write a 1,500-word article targeting "Google Ads optimization" and call it a day. In GEO, you'd expand that to cover the full spectrum of intent by answering why optimization matters, how to measure it, what tools to use, common mistakes, and advanced strategies.
Language matters differently too. SEO keywords are often more formal or search-query-like ("best Google Ads strategies 2025"). GEO content should mirror natural, conversational language, reflecting how people actually speak and ask questions. This aligns with how AI engines interpret and generate responses.
Keywords still matter in GEO, but keyword placement alone isn't enough. You need to pair it with contextual depth, question-based structure, and intent coverage to succeed in the generative search landscape.
Content Structure for SEO vs Answer Chunks for GEO
SEO content structure is designed to guide both users and search engine crawlers through your page. You start with a single H1 that includes your primary keyword. Then you break the content into logical sections using H2 and H3 headings, each targeting a keyword variation or related subtopic.
The structure is hierarchical. The H1 introduces the main topic, H2s divide it into major sections, and H3s provide additional detail where needed. This makes it easy for Google to crawl and understand the page's organization.
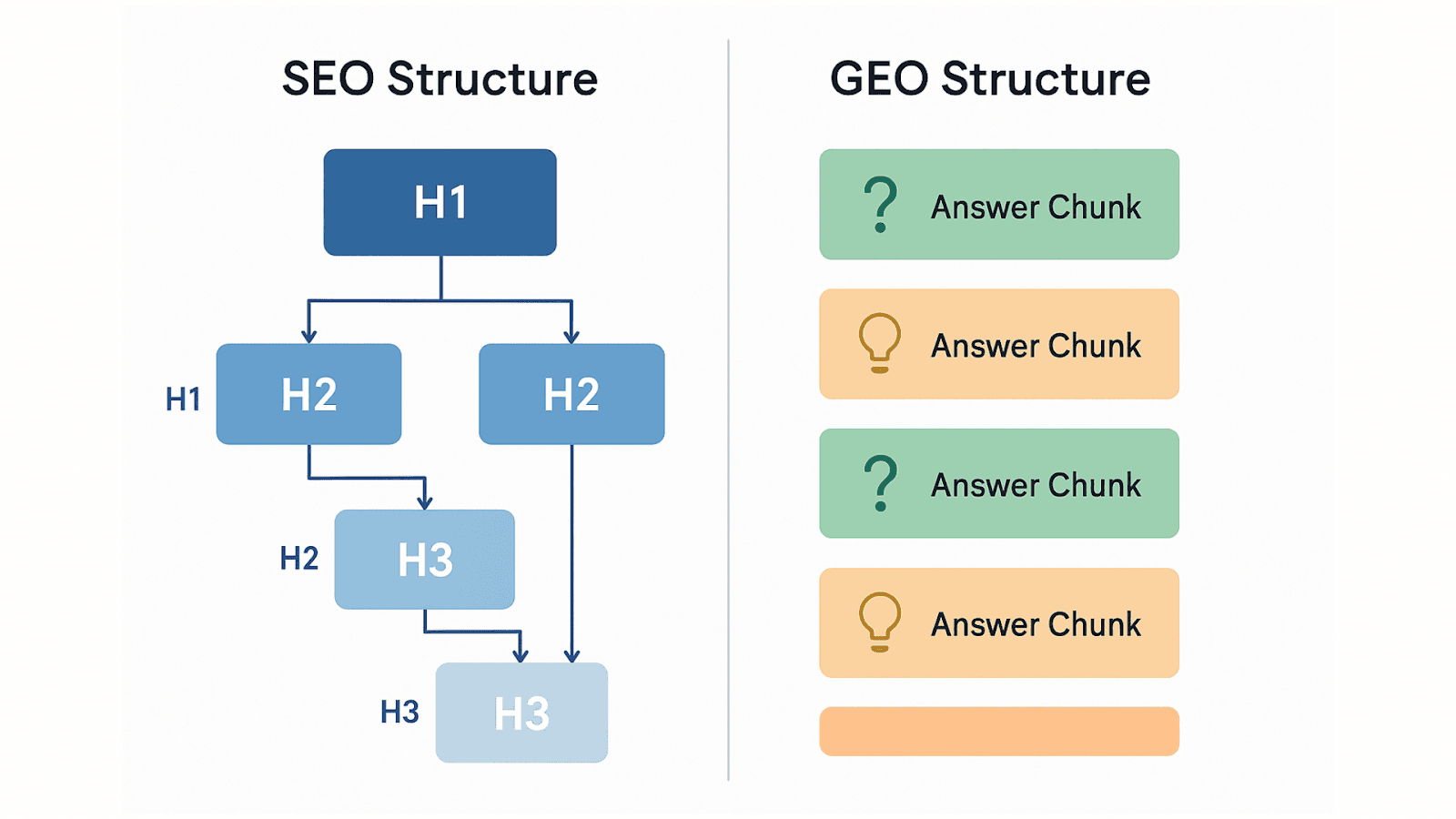
GEO content structure is built around answer chunks. Each section under an H2 or H3 should function as a standalone, extractable piece of information. If an AI engine pulls just one paragraph from your article, it should still make sense and provide value on its own. This means you answer the question upfront, then add context, examples, or supporting details afterward.
For instance, if your H2 is "What is a good CTR for Google Ads?", the first sentence should directly state the answer: "A good click-through rate for Google Ads typically ranges from 3% to 5% for search campaigns, though this varies by industry." Only after providing that clear answer do you expand with explanations or tips.
This approach aligns with how generative engines extract content. They don't always pull entire articles but grab the most relevant chunk that answers the user's query. If your answer is buried three paragraphs deep, it's less likely to be selected.
FAQs and Q&A sections are helpful for SEO but essential for GEO. AI engines love question-answer pairs because they're easy to parse and match user intent. Including a dedicated FAQ section at the end of your article significantly boosts your chances of being cited in AI responses. You don't have to choose one over the other. The best approach is to layer GEO principles onto a solid SEO foundation. Use clear headings, answer questions upfront, break content into digestible chunks, and ensure each section can stand alone.
How Do Backlinks and Authority Signals Work in SEO and GEO?
Backlinks are the currency of SEO. When another website links to yours, it's essentially a vote of confidence. Google interprets these links as signals of trust and authority. The more high-quality backlinks you have, the more likely you are to rank higher in search results.
Not all links are equal. A backlink from a major publication like The New York Times or a .gov website carries far more weight than a link from a low-authority blog. In SEO, building backlinks is a deliberate strategy. You might create shareable content, reach out to industry websites for guest posts, or get featured in roundups and resource lists. GEO values authority differently. Generative AI engines don't rely as heavily on backlinks to determine trustworthiness. Instead, they evaluate authority through content quality, citations, and topical expertise. If your article includes recent statistics, quotes from industry experts, and references to authoritative sources, AI engines see it as credible.
This doesn't mean backlinks are irrelevant for GEO. A well-linked page is still more likely to be indexed and discovered by AI systems. But GEO shifts the focus from how many sites link to you, to how well you demonstrate expertise within your content itself. User-generated content and social proof add another layer of authority in GEO. Including customer reviews, testimonials, or references to community discussions (like Reddit threads or G2 reviews) adds authenticity. AI engines increasingly favor content that reflects real-world experiences, not just polished marketing copy.
External citations matter more in GEO than traditional SEO. If you cite recent data from trusted sources like government reports, academic studies, or major industry publications, it strengthens your content's authority in the eyes of AI systems.
Meta Descriptions and Title Tags for SEO vs GEO
In SEO, title tags and meta descriptions are fundamental on-page elements. The title tag appears as the clickable headline in search results, and it's one of the most important ranking factors. It should be between 50 and 60 characters, include your primary keyword near the beginning, and clearly describe what the page is about.
Meta descriptions, while not a direct ranking factor, influence whether users click on your result. They should be between 135 and 155 characters, include the target keyword naturally, and provide a compelling reason to visit your page. Think of it as a mini sales pitch that tells users why your content is worth their time.
GEO changes how these elements function. AI engines don't always display title tags and meta descriptions in the traditional sense. When ChatGPT or Perplexity generates an answer, there's no SERP to click through. The AI extracts relevant information and presents it directly.
These elements still help AI systems understand your content's topic and relevance, but they don't function as click magnets in the same way. A clear, keyword-rich title tag helps AI engines quickly identify what your content covers. If your title is vague or generic, the AI might skip your page in favor of one with a more explicit, relevant title.
Headings and first sentences become more important in GEO. AI engines scan your H1, H2s, and the opening lines of each section to understand structure and extract answers. Making sure your headings are clear and your opening sentences directly answer the question matters more than perfecting your meta description.
Why Does Q&A Content Perform Better in GEO?
Q&A content aligns perfectly with how AI engines process and present information. When users interact with generative AI tools, they're asking questions in natural language. The AI needs to find content that directly answers those questions in a clear, concise format.
Question-based headings make it easy for AI to identify relevant sections. If your H2 is "How do backlinks affect SEO rankings?", the AI instantly knows that section addresses a specific user query. Content structured around questions gets parsed more easily and accurately by AI systems.
Direct answers get prioritized. When you structure content as Q&A, you're forced to provide straightforward answers upfront. This matches how AI engines extract information. They look for the most direct response to a query, and Q&A format delivers exactly that.
Users ask follow-up questions, and Q&A content anticipates them. When someone searches for information, they rarely stop at one question. They have related queries and want to explore the topic deeper. By including multiple Q&A pairs, you cover the intent spectrum and increase the likelihood that AI will select your content for various related queries.
FAQ sections at the end of articles are particularly valuable for GEO. They allow you to address common questions that didn't fit naturally into the main content. AI engines frequently pull from FAQ sections because they're clearly labeled and easy to extract. Q&A format also improves readability for humans. People scan content looking for answers. When you present information in question-answer format, you make it easier for visitors to find what they need quickly. This benefits both user experience and AI extraction.
Internal Linking Strategies for SEO vs GEO
Internal linking has always been important for SEO. It helps search engines discover and crawl your pages, distributes page authority across your site, and keeps users engaged by guiding them to related content. The standard practice is to use contextual anchor text that includes relevant keywords and link to pages that add value to the reader's journey.
For SEO, you want to create a logical site structure where important pages receive more internal links. This signals to Google which pages are most valuable. You also use internal links to build topical relevance by connecting related articles and creating content clusters around specific themes.

GEO doesn't eliminate the need for internal linking, but it changes how you think about it. AI engines don't follow internal links the same way search engine crawlers do. When an AI extracts content from your page, it focuses on the information within that specific page rather than exploring linked pages.
Internal links still play a role in GEO by providing context and demonstrating topical depth. If you mention AI visibility and link to a detailed guide, it shows that your site covers the topic comprehensively. The bigger shift is that each page needs to be more self-sufficient for GEO. Each article should provide substantial value on its own while still linking to related resources for those who want to explore further.
How to Balance SEO and GEO in Your Content Strategy?
You don't have to choose between SEO and GEO. The smartest approach is building content that performs well in both traditional search and AI-generated results. Start with solid SEO fundamentals because they create the foundation for discoverability. Optimize your title tags, use proper heading structure, target relevant keywords, and build quality backlinks.
Layer GEO principles on top of that foundation. After you've established your keyword strategy and content structure, enhance it by adding Q&A sections, anticipating related queries, and structuring content into extractable chunks. This dual approach ensures you're visible in Google search results while also being citable by AI engines. Think about user intent at both levels. SEO helps you understand what people are searching for. GEO requires you to dig deeper into why they're searching and what follow-up questions they might have. Use traditional keyword research tools alongside AlsoAsked.com and AnswerThePublic to get the complete picture.
Create content that works as both a destination and a source. For SEO, you want users to land on your page and stay there. For GEO, you need content that AI can extract and cite while still driving brand recognition. This means writing clear, authoritative answers that stand on their own while providing enough depth to encourage direct visits.
Measure success differently for each. Track traditional metrics like organic traffic, rankings, and conversions for SEO. For GEO, monitor brand mentions in AI responses, citation rates, and how often your content appears in AI-generated answers. Tools for measuring GEO performance are still evolving, but paying attention to where and how AI systems reference your brand gives you valuable insights.Keep content fresh and updated. Both SEO and GEO favor recent, accurate information. Regularly update your articles with new data, examples, and insights. This maintains your rankings in traditional search while ensuring AI engines continue to see your content as current and trustworthy.
Which SEO Tactics Don't Work for GEO?
Some traditional SEO tactics lose their effectiveness when it comes to GEO. Understanding these differences helps you avoid wasting effort on strategies that won't improve your AI visibility.
Keyword stuffing never worked well for SEO, but it's completely useless for GEO. AI engines understand context and natural language. Repeating the same keyword over and over doesn't make your content more relevant. It just makes it harder to read and less likely to be selected.
Thin content with high keyword density used to rank in some competitive niches. GEO demands comprehensive, in-depth content. AI engines look for authoritative sources that fully address a topic, not pages that barely skim the surface while cramming in keywords.
Link schemes and manipulative backlink strategies don't help GEO. While backlinks still matter for SEO, GEO cares more about the authority demonstrated within your content. Buying links or participating in link exchanges won't make AI engines more likely to cite you.
Optimizing solely for exact-match keywords limits your GEO potential. AI engines interpret intent and context, not just exact phrases. If you're only targeting "Google Ads optimization" and ignoring related queries like "improve Google Ads performance" or "increase Google Ads ROI", you're missing opportunities to be selected for a wider range of searches.
Over-optimization of meta elements doesn't translate to GEO. While meta titles and descriptions still have value, the actual content quality, structure, and directness of your answers matter far more. Ignoring user questions is a critical mistake. GEO requires you to directly address what users are asking. If your content dances around topics without providing clear answers, AI engines will find sources that do.

Emir Erçelen
Sr. SEO/GEO Executive at Visby
Latest posts
Discover other pieces of writing in our blog





